Category:Strain:MG1655
<protect>
| Name |
MG1655 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | |
| Genotype |
F-, lambda-, rph-1 |
| Phenotype |
Reduced (85-90% of rph+ strain) growth rate in minimal medium due to reduced levels of orotatephosphoribosyltransferase (PyrE)[1] |
| Plasmids | |
| Phage | |
| Sources |
CGSC6300. ATCC47076 |
| Construction | |
| References |
|
| edit table |
</protect>
Construction
The original K-12 wild-type strain from the Stanford collection contained both the F plasmid and phage lambda. MG1655 was constructed by curing that strain using acridine orange and UV. [2][3]
Notes
MG1655 is the strain chosen by the Blattner group for the first published sequence of a wild-type laboratory strain of E. coli K-12[4]. Although MG1655 was chosen for having few genetic manipulations from the archetypal E. coli K-12 strain, most strains used in E. coli molecular genetics were not directly derived from MG1655.[2][3] The isolate of MG1655 used for sequence determination is slightly different from the MG1655 stock at the stock center.
rph-1 is a 1 bp deletion that results in frameshift over last 15 codons and has polar effects on pyrE, leading to suboptimal pyrimidine levels on minimal medium. [1]. Although MG1655 can grow in minimal media lacking uracil, adding uracil to the media increases the growth rate by 10-15%.[1]
Isolates of MG1655 from different labs are genetically variable[5][6]. Although the Stock Center isolate used by Soupene et al.[5] contained a deletion around fnr, the isolate currently being distributed by the CGSC is fnr+. MG1655 isolates obtained from the stock center at various times prior to 2000 are also fnr+ (D. Siegele, pers. comm.).
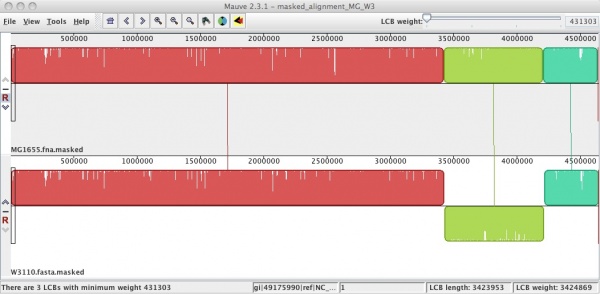
Comparison to W3110
The genomes of MG1655 and W3110 are highly similar, but W3110 contains a large inversion. [7] Below is shown an alignment of these two strains using Mauve. The strains compared were first run through RepeatMasker against a library containing all of the IS elements found in E. coli strains.
Resequencing of MG1655 and comparison to the reference strain
Sequencing of multiple isolates has identified several common genetic variations in strains that are labeled MG1655 in strain collections[8]. Strains CGSC6300 (ATCC 47076), the original MG1655 deposited at CGSC by M.S. Guyer, and CGSC7740 (ATCC700926), the sequenced MG1655 re-deposited at CGSC by F. Blattner, were obtained directly from the ATCC. The table below is adapted from Freddolino et al. [8]
<protect>
| Coordinate | Genomic region | type | MG1655 reference sequence | W3110 reference sequence | ATCC47076 CGSC6300 (MG1655) | ATCC700926 CGSC7740 (MG1655seq) | CGSC4474 (W3110) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
257899 |
Insertion |
G |
G |
G |
IS1 insertion |
G |
||
|
547694 |
SNP |
A |
A |
G |
G |
G |
also in PMID:21555365[9], PMID:21422176[10], PMID:20435762[11] | |
|
547832 |
Insertion |
— |
— |
G |
G |
G |
also in PMID:21555365[9], PMID:21422176[10], PMID:20435762[11] | |
|
1298719 |
oppA-ychE |
Insertion |
T |
T |
T |
IS5 insertion |
IS5 insertion |
orientation different in W3110 |
|
2171386 |
Insertion |
— |
— |
— |
CC |
— |
also in PMID:21422176[10] | |
|
3558478 |
Deletion |
G |
G |
G |
— |
G |
also in PMID:21422176[10], PMID:21719796[12] | |
|
3957957 |
ppiC-yifO |
SNP |
C |
T |
T |
T |
T |
also in PMID:21555365[9], PMID:21422176[10] |
| edit table |
</protect>
See also
References
See Help:References for how to manage references in EcoliWiki. [13]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Jensen, KF (1993) The Escherichia coli K-12 "wild types" W3110 and MG1655 have an rph frameshift mutation that leads to pyrimidine starvation due to low pyrE expression levels. J. Bacteriol. 175 3401-7 PubMed
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bachmann, BJ (1972) Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev 36 525-57 PubMed
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bachmann, B.J. Derivations and genotypes of some mutant derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12. In: Neidhardt, FC et al. (1996) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: Cellular and Molecular Biology (ASM Press, Washington, DC)
- ↑ Blattner, FR et al. (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277 1453-62 PubMed
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Soupene, E et al. (2003) Physiological studies of Escherichia coli strain MG1655: growth defects and apparent cross-regulation of gene expression. J. Bacteriol. 185 5611-26 PubMed
- ↑ Freddolino, PL et al. (2012) Newly identified genetic variations in common Escherichia coli MG1655 stock cultures. J. Bacteriol. 194 303-6 PubMed
- ↑ Hayashi, K et al. (2006) Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2 2006.0007 PubMed
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Freddolino, PL et al. (2012) Newly identified genetic variations in common Escherichia coli MG1655 stock cultures. J. Bacteriol. 194 303-6 PubMed
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Skovgaard, O et al. (2011) Genome-wide detection of chromosomal rearrangements, indels, and mutations in circular chromosomes by short read sequencing. Genome Res. 21 1388-93 PubMed
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Fabich, AJ et al. (2011) Genotype and phenotypes of an intestine-adapted Escherichia coli K-12 mutant selected by animal passage for superior colonization. Infect. Immun. 79 2430-9 PubMed
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Lee, DH & Palsson, BØ (2010) Adaptive evolution of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 during growth on a Nonnative carbon source, L-1,2-propanediol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76 4158-68 PubMed
- ↑ Gubellini, F et al. (2011) Physiological response to membrane protein overexpression in E. coli. Mol. Cell Proteomics 10 M111.007930 PubMed
- ↑ Guyer, MS et al. (1981) Identification of a sex-factor-affinity site in E. coli as gamma delta. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 45 Pt 1 135-40 PubMed
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.