Category:Pathway:TCA Cycle
About
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle serves two roles in E. coli. First, the oxidation of acetyl-CoA primarily from the final product of glycolysis, pyruvate, falls primarily to the TCA cycle. Second, many important precursors for the biosynthesis of amino acids are derived from intermediates of the TCA Cycle.
Overall Pathway
The Reactions
| test | 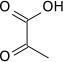
|
Pyruvate | |||||||||
 |
Pyruvate dehydrogenase | ||||||||||
| Acetyl-CoA | |||||||||||
| H2O | |||||||||||
 |
arrow | 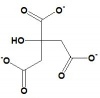 |
arrow | 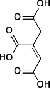 |
 |
 |
Arrow | OxaloSuc image | |||
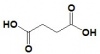
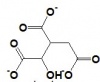
| Oxaloacetate | Citrate Synthase | Citrate | Aconitase | Cis-Aconitate | Aconitase | Isocitrate | Isocitrate Dehydrgoenase | Oxalosuccinate | |||
| Malate Dehydrognease | Arrow | Arrow | enzyme | ||||||||
|
arrow | 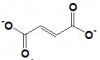
|
arrow | 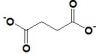
|
arrow | 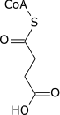
|
Arrow | ||||
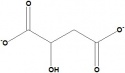
| Malate | Fumarase | Fumarate | Succinate Dehydrogenase (complex) | Succinate | Succinyl CoA-synthetase (complex) | Succinyl CoA | Alpha Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (complex) | 2-ketoglutarate |
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
Pages in category "Pathway:TCA Cycle"
The following 12 pages are in this category, out of 12 total.